|
EXAMPLES OF ANSWERS (w/ FEEDBACK) FOR
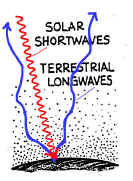
(a) For the
figure arrangement shown you
should have entered Figure
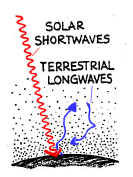
Y (b) You should have drawn a circle around the two BLUE arrows ONLY in FIGURE Y. Together they represent outgoing terrestrial longwave radiation (left blue arrow) being absorbed by greenhouse gases (space in between) and re-radiated back to the Earth's surface (right blue arrow) SOME
EXAMPLES OF GOOD ANSWERS TO (c) (from an earlier exam that contrasted only
Figures Y & Z): (c)
EXPLAIN WHY FIGURE Y is a more accurate depiction of the
natural Greenhouse Effect than Figure Z: Student
1: "I
selected figure Y because the greenhouse gases absorb terrestrial longwaves,
then later emit these longwaves. Figure
Y is a better depiction because it shows that greenhouse gases absorb
terrestrial longwaves, greenhouse gases to not reflect these longwaves back to
Earth." Student
3: "Figure Y accurately depicts the natural
greenhouse effect because it shows the terrestrial longwaves being absorbed by
the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and being radiated back to Earth." Student
4: "I selected Figure Y as it more correctly
illustrates the longwave IR radiation coming from the heat source, the surface
of the Earth, and being absorbed by gases in the atmosphere."
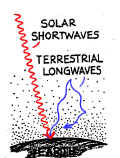
Some good answers telling why FIGURE Z is wrong: Student
1: "Figure
Z is wrong because it shows greenhouse gases reflecting the terrestrial
longwaves back to Earth. Greenhouse
gases do not reflect terrestrial longwaves, they absorb them." Student
3: "Figure
Z is wrong because it shows the terrestrial longwaves being bounced back to the
Earth by the atmospheric greenhouse gases. [This student used the B-word
(bounced) -- would be more scientifically precise to say reflected,
even when describing this incorrect figure.] Student
4: "Figure
Z is misrepresentational because it simply shows the IR bouncing off the
particles, neglecting the actual absorption transpiring." [This one could be refined somewhat. What does the
student mean by "particles?" I
suspect what is meant is the dots in the figure that represent the atmospheric
gases.] (d)
Give a scientifically accurate DEFINITION of the natural
greenhouse effect in your own words: EXAMPLES
OF GOOD ANSWERS -- Note how many creative and original ways the same concept can
be worded! Student
1: "The
greenhouse effect is the absorption of escaping infrared radiation by greenhouse
gases, such as CO2 and H2O, which then emit some of
this radiation back to Earth. This
process warms the planet by preventing some infrared from escaping to
space." Student
2: "The greenhouse effect is the absorption of
terrestrial longwave radiation by greenhouse gases, which is then radiated out
towards the earth." [Note
that this is not a perfect answer because it's not clear what is radiating out
towards the earth. Here's a
slightly better wording: " The greenhouse effect is
the absorption of terrestrial longwave (IR) radiation by greenhouse gases.
The GH gases then radiate the IR back towards the earth."] Student
3: "The
greenhouse effect is a natural process in which terrestrial radiation (IR-longwaves)
is released from the Earth, absorbed by greenhouse gases, and radiated back to
the Earth." Student
4: "The
natural greenhouse effect results from certain gases[']
ability to absorb and emit IR (infrared radiation) at discrete frequencies.
After the Earth has radiated this IR, greenhouse gases absorb this
radiation . . . and reradiate it
back to the surface." Student
5: "The
earth gives off terrestrial radiation (infrared) which is absorbed in the
troposphere by certain gases such as H2O and CO2 which are good absorbers of
infrared radiation (greenhouse gases). These
gases after absorbing the infrared radiation reradiate it back to Earth keeping
the Earth's temperature at the comfortable temperature it is today.
If there was no greenhouse effect and the radiation was allowed to escape
to space, then the temperature of Earth would be too cold to hold life." IGC
Glossary ( p 409): "The
greenhouse effect is the natural mechanism by which the Earth's surface is
warmed by infrared-absorbing gases in its atmosphere."
[Dr H thinks this definition is a good starting point, but it needs to be
developed more. Here's her suggested re-writing of the IGC definition: "The
greenhouse effect is the natural mechanism by which the Earth's surface is
warmed when greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb terrestrial infrared
radiation and then emit the IR radiation back to the Earth's surface."] EXAMPLES
OF ANSWERS WITH ONE OR TWO
PROBLEMS: Student
6: "The
greenhouse effect is the natural mechanism in which the earth's surface is
warmed by IR gases (Infrared Radiation) that are absorbed in the atmosphere then
radiated IR back onto the earth. Without
the Greenhouse Effect the earth would be below freezing temp and life we know
would not exist." [ This answer is pretty good and models itself
after the IGC Glossary definition. However
there is a problem in how it is phrased which leads to a confusion between
infrared radiation (IR) and greenhouse gases.
The answer implies that these two are the same thing, calling them.
"IR gases." There is no such thing as "IR gases." Greenhouse
gases are gases and they do the absorbing of IR radiation -- two separate things
with different roles in the GHE. The IGC Glossary's use of the term "infrared-absorbing
gases" may have been the source of this slight confusion in how the student
presented the answer.] Student
7: "The
Greenhouse effect happens when the earth emits Infrared Radiation upwards, then
some is absorbed by the atmosphere (primarily CO2 and water vapor) and then
reflected back to the earth (longwave radiation). This is needed by the earth or else everything would be
extremely cold." [Can
you identify what's wrong here? The
fatal flaw is the use of the word reflected instead of radiated.
The main IR wavelength ranges involved in the GHE are NOT reflected --
the IR is absorbed and then radiated. There
is a very small band of IR wavelengths (close to visible light) called
Near-IR that can be reflected in the manner that visible light is reflected, but
the IR primarily involved in the GHE is NOT reflected like visible light!
In this answer there is also a suggestion that the student may think that
infrared radiation emitted upward by the Earth is something a bit different than
the longwave radiation sent back to Earth.
As we use the terms in this class, infrared
and longwave radiation are the same thing -- the Earth emits IR /
longwave radiation and the GH gases absorb and emit IR /longwave
radiation as well.] EXAMPLES
OF ANSWERS WITH MAJOR PROBLEMS: Student
8: "The
natural greenhouse effect is when some of the gases that are bounced off earth
does not leave the ozone and circles back to earth.
This is used with gases such as CO2 and H2O."
[This answer has at least two major problems.
First of all GASES are described as "bouncing off the
earth" which is wrong -- even if the student were to use the term
reflecting instead of bouncing, the process of reflection in the context of the
energy balance does not apply to gases. What is reflected
is some of the incoming shortwave (UV and visible) radiation, BUT the GHE does
not involve shortwave radiation, only terrestrial longwave.
Second, for some reason the term ozone is introduced -- but in an odd
way, almost as if ozone is being used as a synonym for the troposphere.
Overall, the answer uses terms and concepts wrong, is poorly phrased, and
presents information that doesn't mean anything.] Student
9: "The
greenhouse effect is due to the depletion of the ozone layer due to high volumes
of CFC's and carbon dioxide. With
combinations of these and water H2O and the radiation of the Sun
"Heat" causes a effect on the atmosphere.
Because we talked about it in class."
[ This answer is looping all over the place. It exhibits a bit of knowledge (link between ozone layer
depletion and high volumes of CFC's) but this
is knowledge that is totally irrelevant to a question about the greenhouse
effect. The greenhouse effect takes
place primarily in the troposphere, while ozone layer depletion is taking place
in the stratosphere. These two
major global change issues are NOT the same thing and are not directly related
,as the student implies. Ozone
and CFC's (when they reside in the troposphere) do play a role in the greenhouse
effect because they are greenhouse gases, but the chemical processes involved in
the depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer are totally different processes
than the radiation processes involved in the troposphere's greenhouse effect
|