GC 170A1 Midterm Practice
Questions- Fall 2014
Printer friendly version
Here is an assortment of practice questions selected from
previous exams that
are good examples of the types of questions that will be
on this
year's
Midterm Exam. I can't give you practice on
every kind of
question I will ask, and on every topic I will ask about,
but these practice questions should help you get an idea of what
the exam will be like and will help you review some key
concepts.
NOTE: For additional practice, review the
questions in the Self Checks & RQ’s, and Test #1 and #2
NOTE:
The exam itself will
not be as
long as this set of practice questions.
It will contain
about 25 multiple choice questions (5 pts each, with the
rest of the questions being, fill-in-the-blank, make-a-sketch,
and a short answer-essay question.
Question
#1 (a, b, & c)
refers to
the figure below which represents a portion of the
Electromagnetic Spectrum with wavelengths shown ( in
micrometers, µm) along
a horizontal line and sections of the spectrum bracketed and
labeled.
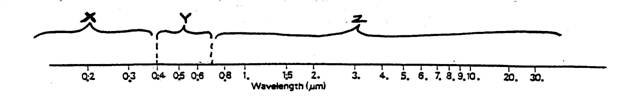
(a)
Which bracketed section of the spectrum
represents visible light? (Circle one) X Y Z
(b) Which bracketed section of the spectrum represents infrared
wavelengths? (Circle one) X Y Z
(c) Which bracketed section of the spectrum represents
ultraviolet wavelengths? (Circle one) X Y Z
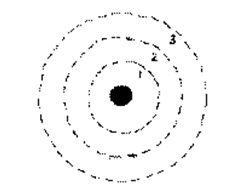
2.
In the dot diagram of the atom shown at
right, Feature X represents one of the atom's
electrons & Feature Y represents the atom's
nucleus. If this atom has a neutral
charge,
how many positively charged
protons does the
nucleus contain:
a) one b) two c)
three d) four
|
 |
3. If a
photon of
electromagnetic energy (with just the right frequency and
wavelength) is absorbed by the electron represented by
Feature X in #2 , which of the following is likely to happen:
a) energy will be absorbed by the photon
b) energy will be emitted by the electron
c) the photon will make a quantum leap to a lower energy level
d) the electron will make a quantum leap to a higher energy
level
4.
The
Earth is heated by incoming radiation from the sun, with the
greatest intensity occurring in the visible (light) part of the
electromagnetic spectrum, and then the Earth cools by radiating
infrared (IR) back out to space through the ozone hole.
(a)
True
(b) False
5.
If it
weren’t for the Greenhouse Effect, the Earth’s average surface
temperature would be well below the freezing point of water.
(a)
True
(b) False
6.
The
Earth’s temperature depends on three main factors.
Which of the following correctly lists these factors:
a) the
Earth's reflectivity, Solar radiation (flux), and clouds
b) the
Earth’s reflectivity, the amount of ice cover on the planet, and
the amount of forest cover
c) the
Solar flux, the Greenhouse Effect, and the ozone layer
d)
the Solar flux, the Greenhouse Effect, and the Earth’s
reflectivity
7.
We
use wave terminology to describe the behavior of electromagnetic
radiation. The relationship between
wavelength
(λ), wave frequency (ν) and
wave speed (c, the speed of
light) can be depicted in equation form as:
c = λ ν
If the wave speed (c)
is constant, which of the
following best describes the relationship between wavelength and
frequency:
a) “the
longer the wavelength, the lower its frequency”
b)
“the longer the wavelength, the higher its frequency”
c)
“the shorter the wavelength, the lower its frequency”
d)
“the shorter the wavelength, the lower its speed”
8.
The atmospheric layers of the troposphere and the
stratosphere are important to global climate change because:
a)
they are the two layers closest to the sun, which is the
source of the Earth’s energy
b)
they are the two layers in which temperature INCREASES
with altitude in the atmosphere
c)
they are the layers in which most of our weather and
heat transfer occur (i.e., in the troposphere) and where
most of the atmosphere’s ozone occurs (i.e., in the
stratosphere)
d)
they are the layers having the lowest atmospheric pressure.
9.
According to the prevailing theories described in your SGC-E
Text text,
the ability of various greenhouse gases to absorb and emit
photons of infrared radiation depends on:
a) the
frequency at which they are rotating compared to the wavelength of
radiation
b) the
amplitude at which they are vibrating compared to the wavelength of
radiation
c) the
number of protons present in the molecule
d) BOTH a
and b can influence which wavelengths of infrared radiation are
absorbed or emitted.
10. Select the
statement below that best states the reason why some of
the gases depicted below are more likely to be
greenhouse
gases than the other gases shown --
according to the
theory of quantum mechanics?
a) Gas 2 and Gas 4 are more likely to be greenhouse gases
because the rotation, vibration, and bending behavior of their
symmetric diatomic structure can occur at discrete
frequencies that allow the absorption and emission of IR
(infrared)
electromagnetic wavelengths
b) Gas 2 and Gas 3 are more likely to be greenhouse gases
because they rotate and don't bend
and rotation
at discrete frequencies is associated with the
absorption
and emission of IR (infrared) electromagnetic wavelengths
c) Gas 1 and Gas 3 are more likely to be greenhouse gases
because the rotation, vibration, and bending behavior of their
asymmetric triatomic structure can occur at discrete
frequencies that allow the absorption and emission of IR
(infrared) electromagnetic wavelengths
d) None of these figures illustrates a greenhouse gas, because
the figures show molecules only and the absorption and
emission of IR (infrared) electromagnetic wavelengths occurs
within atoms (not molecules) when electrons absorb
and emit IR photons
of radiation.
11. Which of the following is
one of the five most
abundant gases in the Earth’s atmosphere
AND is also
a greenhouse
gas?
a) Argon (Ar)
b) Carbon dioxide (CO2) c) Ozone (O3)
d) Nitrogen (N2)
12.
Which of the following is a
CORRECT statement about the difference between
ultraviolet (UV) electromagnetic radiation and
infrared (IR)
electromagnetic radiation?
a) UV electromagnetic radiation has a
shorter wavelength
and lower frequency than IR electromagnetic
radiation
b) UV electromagnetic radiation has a
higher energy
and higher frequency
than IR electromagnetic
radiation
c) UV electromagnetic radiation plays
a more primary role
in the greenhouse effect than IR radiation
d) UV electromagnetic radiation is
closer in the
electromagnetic spectrum to microwave, radar, and radio
frequencies than is IR radiation
13. One of the Radiation Laws -- called Wein's Law
-- is a statement about the relationship between the
temperature of a substance and the
wavelength
at which radiation from that substance is emitted. Which of the
phrases below CORRECTLY states the "rule" for Wein’s Law?
a) The
wavelength of radiation a body gives off is
proportional to the fourth power of its absolute
temperature.
b)
Shorter wavelengths involve
higher intensity
radiation fluxes than longer wavelengths
c) The
hotter the temperature of the body, the
longer the wavelength maximum emission of radiation from
that body.
d) The
hotter the temperature of the body, the
shorter the wavelength of maximum emission of
radiation from that body.
14. Now circle the letter of the symbolic notation
(formula) that best represents what Wein's Law is saying (refer
to #13).
Key to notation: [ E = radiation
emitted, T = temperature, λ = wavelength, a = a constant]
a) λ = aT
2
b)
E = a T 4
c) λ = a/T
d) E = λ / a
QUESTIONS
#15 through #
17 refer to the figure below:
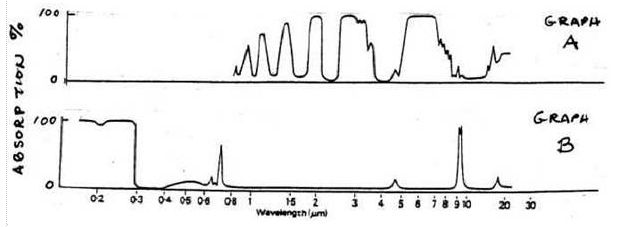
15.
Which one of these phrases based on the Radiation Laws best
explains why absorption bands exist?
a) The amount of radiation passing through a unit
area is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of that area from the source
b) All substances emit wavelengths of radiation as long as their
temperature is above absolute zero.
c) As substances
get hotter the wavelength at which radiation is emitted will
become shorter.
d) Some substances emit and absorb radiation at certain
wavelengths only.
16. GRAPH A
depicts absorption by a gas that absorbs electromagnetic energy
that is mostly:
a) in the visible light part of the spectrum
b) ultraviolet radiation
c) infrared radiation
d) microwave radiation
17.
GRAPH B depicts absorption by a gas that
absorbs electromagnetic radiation that is:
a) mostly longwave radiation
b) mostly infrared radiation
c) both solar and terrestrial radiation
18. Which of the following best states the
differences between solar (Sun) and terrestrial (Earth)
radiation in terms of the
electromagnetic spectrum:
a) The Earth emits most of its radiant
energy as short-wave radiation (< 1 micrometer) while the sun’s
radiation
peak is in the long-wave (>1 micrometer) portion of
the spectrum.
b) The Earth’s radiation peak is in the ultraviolet portion of
the spectrum while the sun’s radiation peak is in the
visible light portion of the spectrum.
c) The Sun’s wavelength of peak emission is about 0.5
micrometer while the Earth’s wavelength of peak emission
is about twenty times longer at about 10
micrometers.
d) Solar radiation involves the greenhouse effect, which
operates mostly in the visible part of the spectrum, while
terrestrial radiation does not involve the
greenhouse effect.
e) The Sun radiates only in the visible light
part of the spectrum while the Earth radiates only
in the infrared part of
the spectrum.
For
QUESTIONS #19 through
#21: Fill in the blank with letter a, b, c, or
d
to match each of the following statements about forms of
energy transfer with the proper process, depending on
which type of energy transfer best represents the statement.
a) Convection b)
Conduction c) Electromagnetic Radiation
19. ____ energy
transfer by means of vibrational energy from one molecule to
the next through a substance.
20. ____ the
predominant form in which energy involved in the Greenhouse
Effect is transferred
21. ____ energy
transfer by means of large-scale movements of material
within a fluid
22.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can
be classified by wavelength range into three types of radiation:
UVA with a wavelength range of 320-400 nanometers (nm), which is
equivalent to .32 -.40 micrometers (μm), UVB
with a range of 290-320 nm or .29-.32
μm, and UVC
with a range of 200-290 nm or .20 - .29 μm.
Which of the following statements about these UV
ranges is correct:
a)
UVC radiation is relatively harmless to life while UVA
radiation is extremely harmful
b)
UVC is the most harmful wavelength range because its
wavelengths are the shortest and therefore the highest energy
wavelengths
c)
UVA is the same UV radiation range that is almost
completely absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere.
d)
On the electromagnetic spectrum, UVC radiation is closer
to visible light than UVB radiation
Questions 23 –26
Referring to the
diagram at left, give the names of the following layers of the atmosphere:
|
23. The layer from A to B is
named: _________________________
24. The layer from B to C is
named: ________________________
25. The layer from C to D is
named: _________________________
26. The layer above D is named:
_________________________
|
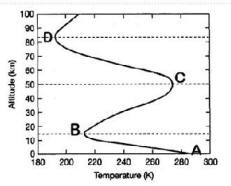 |
27.
At RIGHT is a
figure showing a “mystery
something” which is varying with
altitude in the Earth’s atmosphere, but the label on the horizontal
axis is missing!
Select the choice below which is
the most likely label for
the horizontal axis of the figure:
[HINT: figure out the altitude of the TROPOPAUSE from the
figure for Questions
# 23-26. ]
a)
The figure is showing how
atmospheric pressure varies with
altitude, with the greatest pressure at ~ 30 km.
Therefore the label for the horizontal axis should be
Air Pressure.
b)
The figure is showing how the concentration of one of the primary
greenhouse gases varies with altitude, with a primary peak at ~ 30
km in the troposphere.
Therefore the label for the horizontal
axis should be CO2 Concentration.
c)
The figure is showing how the concentration of
ozone (O3)
varies with altitude,
with the greatest concentration in the
stratosphere.
Therefore
the label for the horizontal axis should be
Ozone Density.
d)
The figure is showing
how temperature varies with altitude, with warm temperatures at
the Earth's surface, even warmer temperatures in the mid-troposphere ,,
and the coolest temperatures near the top of the troposphere.
Therefore the label for the horizontal axis should be
Air
Temperature.
28.
Which
of the following best describes the kind of global change
revealed by the Keeling Curve show at right:
|
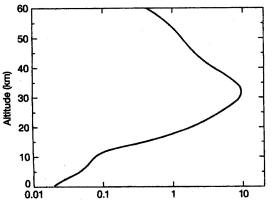
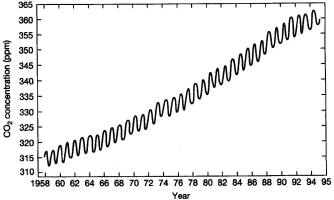 |
a) The Keeling Curve indicates
that carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere has
experienced an increase in variance since 1958, in
addition to annual quasi-periodic oscillations of CO2 that
occur due to seasonal variations in global photosynthesis and
respiration.
b) The Keeling Curve indicates
that carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere has
experienced an increasing trend since 1958, in addition
to annual quasi-periodic oscillations of CO2 that occur due
to seasonal variations in global photosynthesis and respiration.
c)
The Keeling Curve indicates that carbon dioxide
concentration in the atmosphere has experienced a
constant
mean over time since 1958, except for the annual
quasi-periodic
oscillations that occur due to seasonal variations in global
photosynthesis and respiration.
d)
The Keeling Curve indicates that carbon dioxide
concentration in the atmosphere has experienced
can abrupt
step change and an
increasing variance (range of
fluctuations) since 1958, due to seasonal variations in global
photosynthesis and respiration.
|
29.
The graph at right shows
how the temperature of one gram of H2O
changes as calories of heat energy are added to the H2O.
|
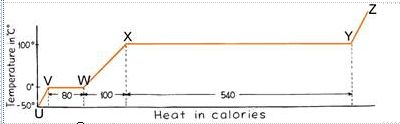 |
Using the graph to help you,
select the
one statement below that best describes the relationship
between the concepts of
Latent Heat (LE),
Sensible Heat (H),
and
phase changes (changes of state)
in H2O:
a)
Segment W-X
of the graph indicates that 100 calories of energy are being
added to one gram of H2O
without changing the temperature
of the H2O
at all. This energy is called
Latent Heat (LE).
b) A
comparison
of Segment V-W with
Segment X-Y
of the graph indicates that it takes
much more energy
(in calories of LE) to create a
phase change from
liquid to vapor
than it does to create a
phase change from
ice to liquid.
c)
Segments U-V, W-X, and Y-Z
of the graph indicate that, even though
calories of energy are added to one gram of H2O,
the H2O
does not change its temperature
and heat up. This is because the energy being added in
represents LE
and is being used to
change the state
of the H2O
from solid to liquid, or liquid to vapor.
d)
Segments V-W and X-Y
of the graph represent sensible heat
(H), while
Segment W-X
of the graph represents latent heat
(LE). Only
Segment W-X
represents a
phase change.
30.
Energy
transfer by means of large-scale movements of material within a fluid
(liquid or air) occurs in which one
of the following processes:
a) convection b)
conduction
c)
latent energy
d)
terrestrial
infrared radiation
e)
shortwave solar radiation
31.
Energy transfer by
waves or pulses of energy that involve
photons occurs in
which one of the following processes:
a) sensible heat
b)
convection
c)
conduction
d)
shortwave solar radiation
32.
Specific
heat
is the amount of energy (in calories) that is needed to raise
one gram of a substance one degree Celsius.
The specific heat of
water
= 1.0 calorie and the specific heat of
sand = 0.20
calorie.
If
we add the
exact same amount of energy to one gram
of water having a temperature of 15ºC and one gram of
sand having a temperature of 15 ºC, which of the following is
most likely to be true?
a)
the sand
and water will both heat up to the same temperature in
the same amount of time
b)
the sand will heat up faster and reach a warmer
temperature than the water
c)
the water will heat up faster and reach a warmer
temperature than the sand
d)
all of the energy going into the water will go into the
latent energy form, hence the
water won't heat up at
all
33.
In the figures below, which
circled area is
the best depiction of the GREENHOUSE EFFECT?
[HINT: The best depiction will be a circled area that
includes the correct type of radiation (shortwave or longwave)
and illustrates absorption and re-radiation of that radiation]
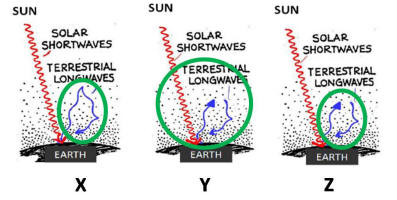
a) the area circled in
Figure X
b)
area circled in Figure Y
c)
area circled in Figure Z
d) none of the figures
show the GREENHOUSE EFFECT exactly as we have
seen it and discussed it in class
34.
Which energy flow diagram below is best depicts
the diagram of a well-designed, highly energy efficient
LED light bulb?
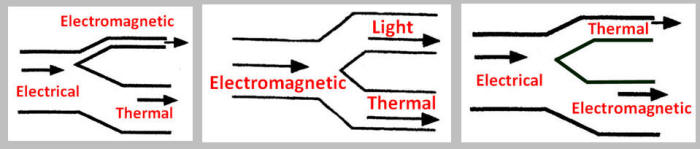
( a )
( b )
( c )
|
|
35.
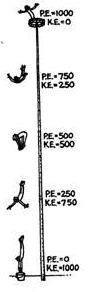
The diagram at left shows the relative amounts
of potential energy (PE)
and
kinetic energy (KE)
that are involved in a diver’s plunge to the ground.
In the diagram, the fact that KE + PE = 1000 at each
point in time (even though the values of KE and PE
change) represents
which one of the
following LAWS of physics:
a) 1st Law of Thermodynamics: “In an isolated system
the total amount of energy is conserved, although energy
may change from one form to another.”
b) The Inverse Square Law
c) The Law of Gravity
d) 2nd Law of Thermodynamics: “Every isolated system
becomes disordered with time.”
|
|
|
|
|
36.
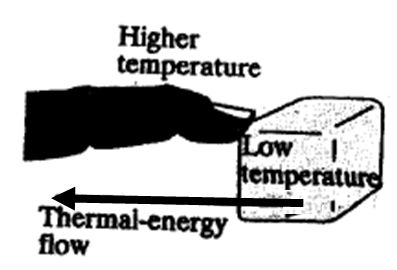
Select the statement that properly describes the figure at
right:
a)
The figure is a good depiction of the 1st Law of
Thermodynamics
=
"In an
isolated system the total amount of energy is conserved,
although energy may change from one form to another over
and over again."
b)
The figure is a good depiction of the
2nd Law of
Thermodynamics = "Energy flows from a higher-temperature
object to a lower-temperature object. It will not spontaneously
flow the other way."
c) The figure is a an incorrect depiction of the
1st Law of Thermodynamics because there is no change of
energy going on in the figure
d) The figure is an incorrect depiction of the 2nd
Law of Thermodynamics because the thermal energy flow
is going in the wrong direction.
|
 |
SAMPLE SHORT ANSWER -ESSAY QUESTION:
(and a few more multiple choice too!)
37.
In class we discussed these three "cartoon" figures and selected one that is a
more accurate depiction of the processes involved
in the natural greenhouse effect.
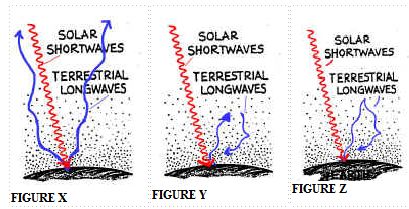
(a) Which figure
above is the more accurate depiction of the natural
greenhouse effect?
Figure ____
(b) On the figure
you selected, CIRCLE the part of the diagram
which represents the energy processes DIRECTLY involved
in the greenhouse effect.
(c)
Explain WHY the figure you selected is a
more accurate
depiction of the natural Greenhouse Effect
than the
other two figures.
(d) Finally, give a
precise and scientifically accurate
DEFINITION of
the natural Greenhouse Effect in your own
words.
[NOTE:
By "natural greenhouse effect" I mean the naturally
occurring greenhouse effect, not the "enhanced
greenhouse effect" that arises from anthropogenic
activities such as humans increasing the concentration
of greenhouse gases by burning fossil fuels].
38.
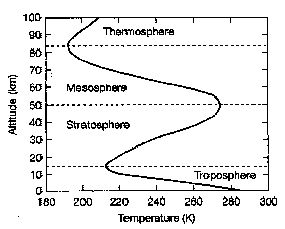
In the diagram below, the layer of the
atmosphere where the Greenhouse Effect has its
greatest influence is the:
a)
troposphere b) stratosphere
c) mesosphere d) thermosphere
 |
ANOTHER
SAMPLE ESSAY QUESTION:
39.
Briefly explain
what causes the change in temperature with height in
each of the following layers:
a)
the troposphere decreases in temperature with
height because:
b) the
stratosphere
increases in
temperature with height because:
|
40. FILL IN THE BLANKS with
one of the following terms to complete each sentence
properly.
conduction
convection
radiation
sensible heat
latent heat
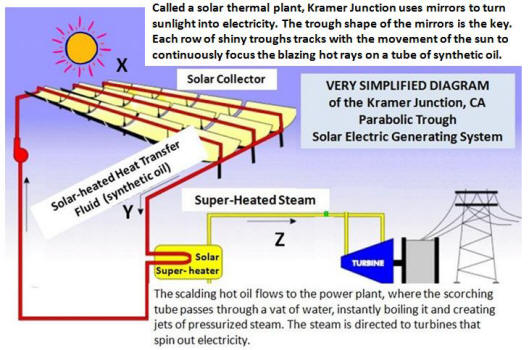
The diagram at right is a greatly simplified version of how the large
southern California solar power plant at Kramer Junction
(in the Saved by the Sun video) generates
electricity from solar energy.
(a) ENERGY is transferred from X-to-Y (from the
SUN to the SYNTHETIC OIL in the red tubes) by
____________
(b) When water in the Solar Super-heater
vat boils
instantly, the Y-to-Z heat transfer that occurs
can be described as the transfer of ________ in
the SYNTHETIC OIL to _________ in the STEAM .
|
 |
SAMPLE MAKE-A-SKETCH
QUESTION:
|
41.
On the diagram, illustrate
photon
behavior by
MAKING A SKETCH
which shows
what happens when an electron in an excited state
drops to a lower energy level.
Then
LABEL your sketch to identify the
names of all the features you have drawn in.
|
 |
42.
On the blank graph below, sketch in a line that represents the
absorptivity of a hypothetical atmosphere that has
NO
ability to absorb visible light OR infrared
radiation, but CAN absorb ALL
ultraviolet radiation
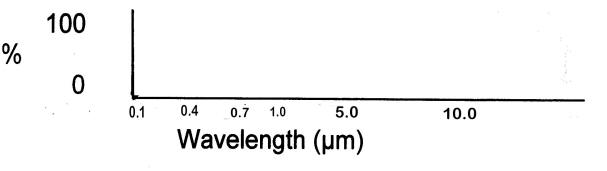
|
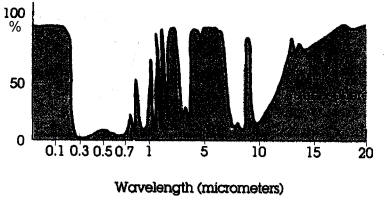
43a.
DRAW A CIRCLE
around the UV+ visible
light atmospheric window region on this absorption curve
for the whole atmosphere and explain WHY this
wavelength range is referred to as an "atmospheric
window.”
43b. Next, DRAW A CIRCLE
around the
IR atmospheric
window region and
explain what is happening in this window
and WHY it is so
important for the Earth's Energy
Balance.
|
|
44.
If
exactly the same amount
of solar energy
was delivered to the lake
surface and the land surface on a sunny day,
what would the surface
temperature be like at sunset?
(a) the land surface would be hotter,
(b) the lake surface would be hotter,
(c) the surface temperature of the land
and lake would be the same
Explain the reasons
for answering as you did.
Would the surface you selected above still be hotter than the
other surface at dawn the next day?
Why or why not?
|
 |
|
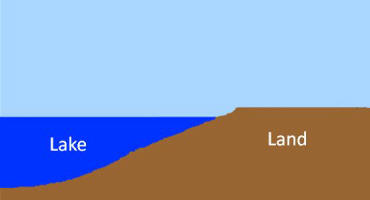
45.
Complete the RADIATION
BALANCE EQUATION by filling in the proper cartoon
symbols in the blanks:
Rnet
= _______ + _______ -
_______ - ________ + _______
= ______ + ______
+ G
46.
Energy
transfer by waves or
pulses of energy that involve photons occurs in
which one of the following processes:
a)
H
in water
b)
Specific
Heat
c)
 d) inertia
d) inertia
In your own words, explain your
answer .
|
47. Trucks and SUVs are
massive vehicles which tend to consume a lot
of gas and are far less fuel efficient than
smaller, less massive compact and subcompact
cars, especially in stop-and-go traffic.
In your own
words, explain WHY in terms of one or both
of the Laws of Motion stated for you below.
Newton's 1st Law
states that all bodies have inertia and that
a body's mass is the measurement of the
inertia. The 1st law also states that a
moving object will continue moving in a
straight line at a constant speed unless
acted on by a force.
Newton's 2nd law can be
written F = ma and says that acceleration
(a) of a body is directly proportional to
the net force (F) acting on the body and
inversely proportional to the mass (m) of
the body.
|
|
|
ANSWER KEY
|